Consumption of antimicrobials in food-producing animals
Finnish Medicines Agency Fimea has monitored the sales of veterinary antimicrobials in Finland since 1995 based on the information provided by pharmaceutical wholesalers. Fimea publishes data annually, expressed by unit of weight (kg of active ingredient). Reporting sales in units of weight does not, however, reflect changes in animal population.
Information, in proportion to the number of food-producing animals, on the consumption of veterinary antimicrobials is mainly available from Europe. According to European reports, published since 2010, the sales of antimicrobials used in food-producing animals are very moderate in Finland. Total consumption between the extremes can differ by one hundred fold in this respect. The proportion of antimicrobials critically important to human medicine is low in Finland.
Total sales of antimicrobials in proportion to the number of food-producing animals and sales of antimicrobials critically important to human medicine in 31 EU/EEA countries in 2022 (mg/PCU, milligrammes of active ingredient per population correction unit)1
| Range of results from 31 countries | Finland | |
| Total consumption | 2.1 – 254.7 | 14.9 |
| 3rd and 4th generation cephalosporins | 0 – 0.5 | <0.01 |
| Fluoroquinolones | 0 – 12.6 | 0.1 |
| Macrolides | 0 – 28.8 | 0.2 |
| Polymyxins | 0 – 10.2 | Have never been used in food-producing animals in Finland |
1 mg/PCU is a technical unit. It describes the consumption of antimicrobials in proportion to the number of major food-producing animals. The need for medication varies greatly between animal species. Therefore variations in the distribution of food-producing animals between different countries should be taken into consideration when the results are explored. Sources: (1) European Medicines Agency, European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption, 2022. Sales of veterinary antimicrobial agents in 31 European countries in 2022. (EMA/795956/2022), Thirteenth ESVAC report, 2023. Cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, polymyxins: p. 27. Link to report (2) Critically important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine 5th revision 2016, World Health Organisation, Link to report
Total sales of antimicrobials in proportion to the number of production animals in 31 EU/EEA countries in 2022 (mg/PCU, milligrammes of active ingredient per population correction unit)1
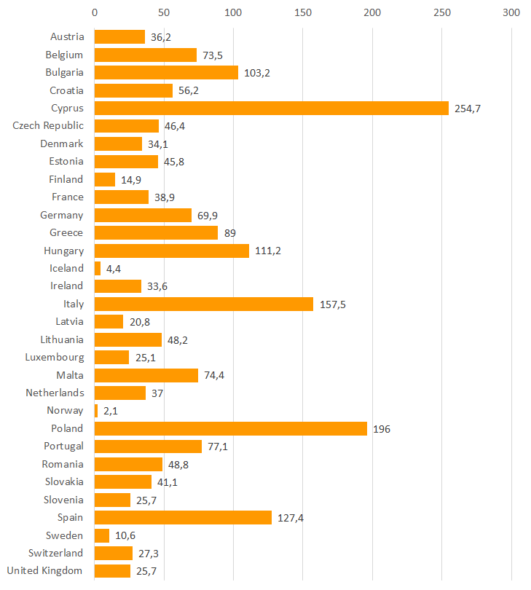
Note: Account should be taken of different populations of food producing animals in different countries when examining the results. The results of different countries are not comparable as such.
As one pharmaceutical product may have several target species, the amount of medicine used per species cannot be differentiated on the basis of sales data. Data on the use of antimicrobials per species would make it possible to investigate which species require the most use of antimicrobials, and how many animals are actually medicated. The only information currently available (2018) is that published by the poultry industry on the use of antimicrobials for meat poultry. According to this data, antimicrobials have not been used in treatment of broiler chickens in Finland since 2009.
Although data specific to different animal species cannot be determined on the basis of the current method, it is possible to determine whether the medicine is administered to individual animals or groups of animals based on the pharmaceutical form in question. Individual medication is favoured in Finland, whereas in the joint results for Europe, most antimicrobials were administered to animal groups in feed or drinking water. In 2016, the proportion of injection products and other pharmaceutical forms used in individual medication was 60% in Finland, while in Europe, 90% of antimicrobials sold for use in food producing animals were administered to groups of animals.
The use of antimicrobials for animals has been strictly regulated for decades. In Finland, antimicrobials are prescription only medicines and a veterinarian is not allowed to a profit on the medicines sold or used. Finland voluntarily gave up the use of antimicrobials as growth promoters soon after Sweden in 1996. In the EU, the use of antimicrobials as growth promoters was gradually prohibited from the late 1990s, with a complete ban being imposed in 2006. In the United States, the transition period to end the use as growth promoters is in progress. According to the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE), in 2015 the use of antimicrobials as growth promoters was allowed in 26% of the countries responding to the survey. Due to the low response rate, the result can be considered as indicative only.
Finland has invested in providing guidance on the prudent use of antimicrobials in animals. The first recommendations on the use of antimicrobials per animal species were issued in 1996. These were ahead of their time in international terms. The recommendations have been updated three times: in 2003, 2009 and 2016. Adopted in 1999, the policy of banning and limiting the veterinary use of certain antimicrobials critically important to human medicine was also significant. Since 2014, the veterinary use of other antimicrobials has also been regulated by legislation. When using antimicrobials, veterinarians must ensure the clinical or microbiological diagnosis, particularly in repeat treatment or when medicating animal groups. The new regulations also prohibit the preventive use of antimicrobials, without veterinary medicinal grounds for doing so.
A strong regulatory basis, determined guidance and focus on food-producing animal health care and the prevention of infectious diseases in animals have yielded results. The use of antimicrobials for food-producing animals is highly moderate in Finland in international terms.
The text is based on the lecture summary ‘Consumption of veterinary antimicrobials in Finland and internationally’ (K. Kivilahti-Mäntylä), the Annual Veterinary Congress Lecture Collection 2016.
Links
Antimicrobial Consumption ESVAC project on Fimea website
Animal medication (Finnish Food Authority)
European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption (ESVAC)
Use of antibiotics in broiler production in Finland 2007-2021 (ETT)
Database tables
Annual sales of veterinary antimicrobial agents for food-producing species
Photo in upper edge: Pixabay
