Anthocyanin concentrations of Arctic bilberries are high in comparison with other berries, about 3 to 5 times higher than those of cultivated blueberries. Anthocyanins are the bioactive compounds and blue and purple pigments in the skin and internal parts of the berries. As cultivated blueberries are light inside, the difference between the two species is considerable.

Photo: Marjo Räisänen, Arktiset Aromit ry
Anthocyanins have been proven to have many health-promoting effects. Scientific research has provided evidence of the preventive effect of anthocyanins as regards cardiovascular diseases, inflammations, and degenerative diseases related to ageing. The anthocyanins in berries have also been proven to promote cognitive functions and eye health.
The Finnish climate is cool. In the middle of summer, southern Finland has 19 hours of daylight and the sun does no set above the Arctic Circle in the north. Research results prove that levels of anthocyanins increase when there are more daylight hours. The anthocyanin levels of wild bilberries are high throughout Finland.
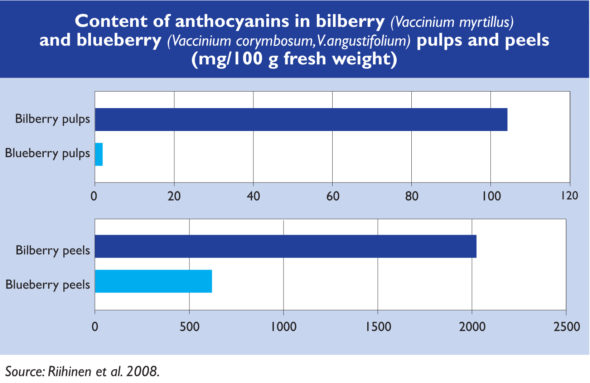
Source of chart: Arktiset Aromit ry. The chart is based on Riihinen K, Jaakola L, Kärenlampi S, Hohtola A. Organ-specific distribution of phenolic compounds in bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) and ”northblue” blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum x V. angustifolium). Food Chemistry 2008;110:156-160
Photo in upper edge: Pixabay/ChadoNihi
